Click here and press the right key for the next slide.
(This may not work on mobile or ipad. You can try using chrome or firefox, but even that may fail. Sorry.)
also ...
Press the left key to go backwards (or swipe right)
Press n to toggle whether notes are shown (or add '?notes' to the url before the #)
Press m or double tap to slide thumbnails (menu)
Press ? at any time to show the keyboard shortcuts
The Puzzle of Moral Foundations Theory
puzzle
If the evidence for cultural variation in moral psychology is at best weak,
and if the theoretical argument for moral reframing is flawed,
why does moral reframing seem to work?
1. ‘Moral convictions and the emotions they evoke shape political attitudes’
2. There are at least two foundational domains of human morality, including harm and purity.
3. ‘liberals and conservatives possess different moral profiles’
4. ‘liberals express greater levels of environmental concern than do conservatives in part because liberals are more likely to view environmental issues in moral terms.’
5. ‘exposing conservatives to proenvironmental appeals based on moral concerns that uniquely resonate with them will lead them to view the environment in moral terms and be more supportive of proenvironmental efforts.’
‘Why does moral reframing work?
The primary explanation is that morally reframed messages are influential because targets perceive a “match” between their moral convictions and the argument’ (Feinberg & Willer, 2019, p. 4).
Why does perceiving a match increase willingness to mitigate climate change?
Feinberg & Willer (2013): because it increases the probability that you will think of climate change as an ethical issue.
?
Why does moral reframing work?
hypothesis 1
match
targets perceive a match
hypothesis 2
source
targets identify the source as an in-group
and so construe the issue as an ethical one
and so construe the message favourably
evidence: Fielding, Hornsey, Thai, & Toh (2020)
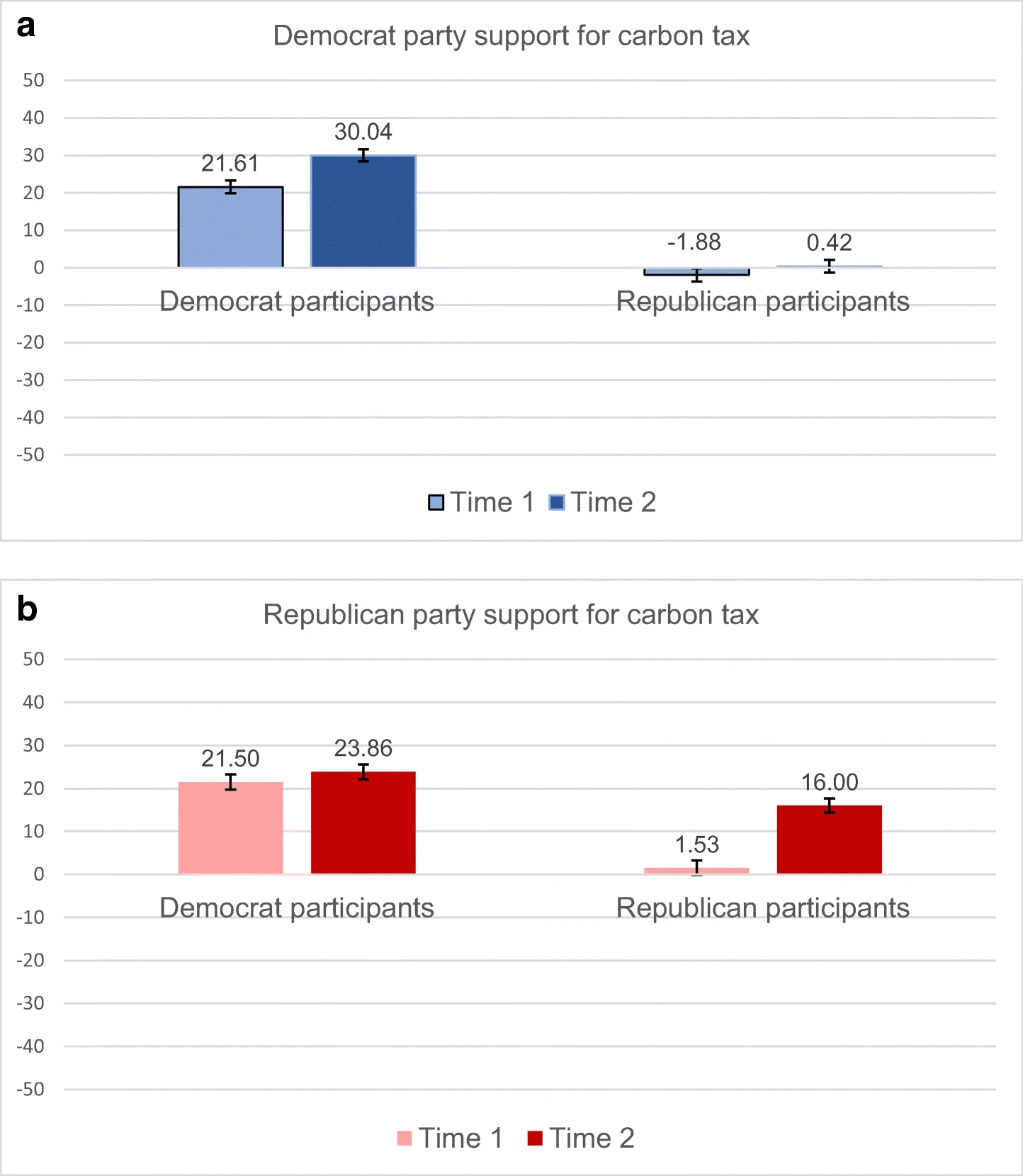

Fielding et al. (2020, p. figure 1)
‘it is possible that the values framing in past studies worked because it provided conservatives with information about the source of the message: when messages aligned with conservative values, Republicans [conservatives] filled in the gaps and simply presumed that the message came from a Republican source’ (Fielding et al., 2020, p. 196).
Why does moral reframing work?
hypothesis 1
match
targets perceive a match
hypothesis 2
source
targets identify the source as an in-group
and so construe the issue as an ethical one
and so construe the message favourably
evidence: Fielding et al. (2020)
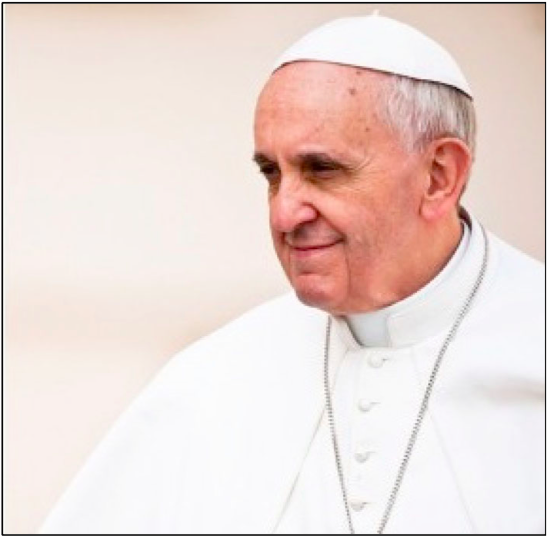

Schuldt et al, 2017
How much do you know about Pope Francis’ views on climate change? [inexact wording]
‘Do you consider climate change to be a moral or ethical issue?’
Results
‘Whereas a minority (46%) of respondents reported perceiving climate change as a moral issue in the control condition, this figure rose to 51% among those in the pope prime condition’ (Schuldt, Pearson, Romero-Canyas, & Larson-Konar, 2017).
‘the pope prime exerted a stronger effect on the moral beliefs of Republicans
‘Democrats were equally likely to report perceiving climate change as a moral or ethical issue regardless of condition’
Why does moral reframing work?
hypothesis 1
match
targets perceive a match
hypothesis 2
source
targets identify the source as an in-group
and so construe the issue as an ethical one
evidence: Wolsko (2017)
and so construe the message favourably
evidence: Fielding et al. (2020)
‘common in-group’
‘a large number of both liberal and conservative politicians, scientists, executives, and religious leaders have argued that traditionally conservative values are extremely well-suited for protecting the natural environment. Traditional conservative values that have been favored include:
1 Demonstrating your patriotism by protecting our natural environment
2 Taking personal responsibility — for yourself and for the land you call home
[...]
5 Respecting your elders and teaching your children good values’
(Wolsko, 2017, p. 290)
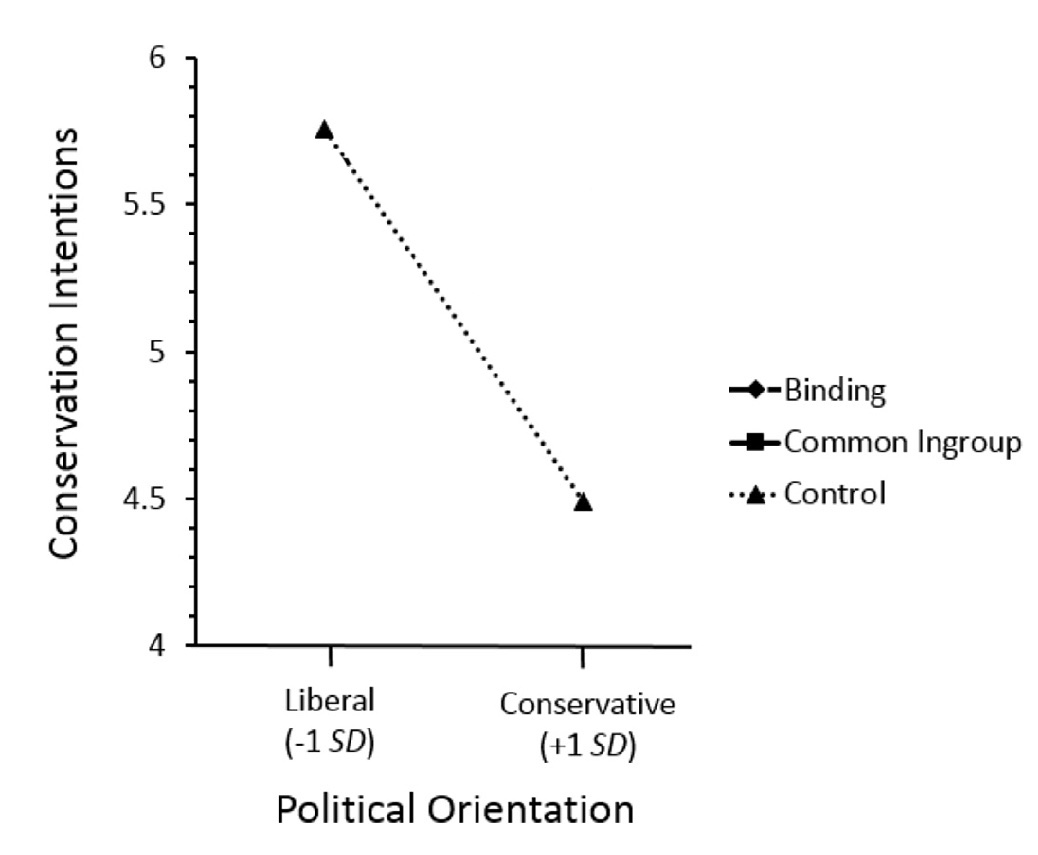
(Wolsko, 2017, p. figure 5)
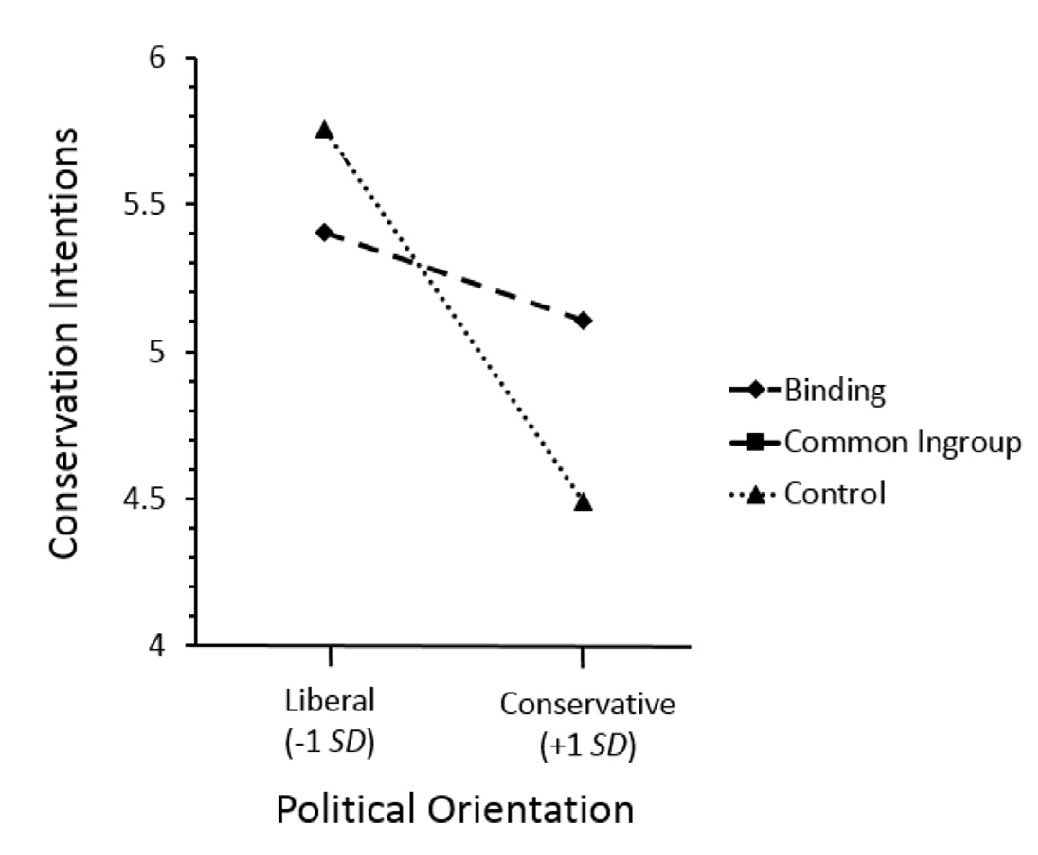
(Wolsko, 2017, p. figure 5)
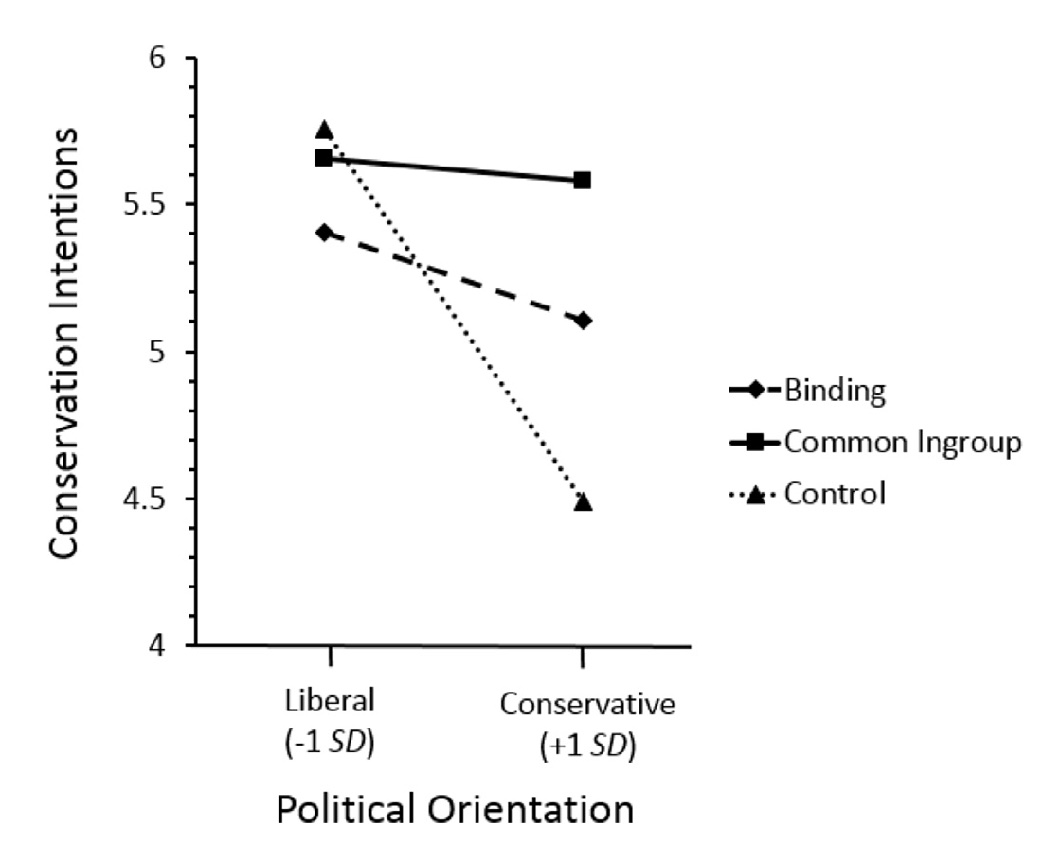
(Wolsko, 2017, p. figure 5)
Why does moral reframing work?
hypothesis 1
match
targets perceive a match
hypothesis 2
source
targets identify the source as an in-group
and so construe the issue as an ethical one
evidence: Wolsko (2017); Miles (2016)
and so construe the message favourably
evidence: Fielding et al. (2020)
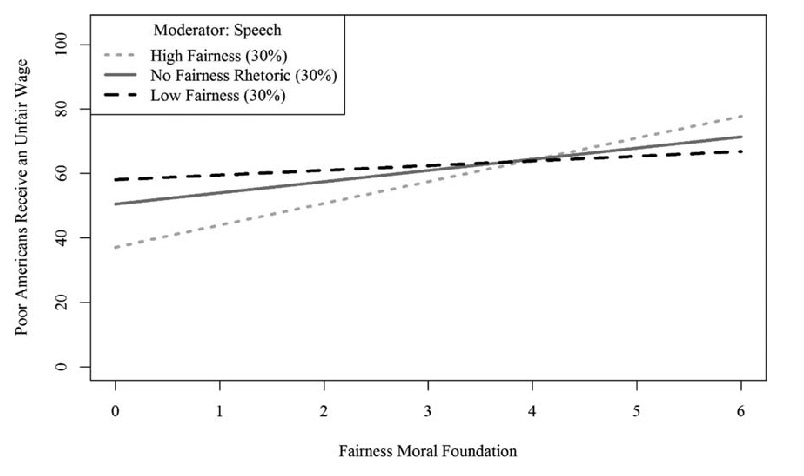
Miles (2016, p. figure 1)
‘conservatives high in Fairness are more supportive of policies proposed by President Obama than liberals who are low in Fairness’
further evidence: food-waste
Wasting is food linked to believing it morally wrong to do so
Harm-based messages e.g., “Food waste harms the environment”
influence those who rank harm highly to waste less
vs
Disgust-based messages e.g., “Food waste attracts dirty animals and pests”
influence those who rank purity highly to waste less.
(Bretter et al., 2023)
Why does moral reframing work?
hypothesis 1
match
targets perceive a match
hypothesis 2
source
targets identify the source as an in-group
and so construe the issue as an ethical one
evidence: Wolsko (2017); Miles (2016)
and so construe the message favourably
evidence: Fielding et al. (2020)
puzzle
If the evidence for cultural variation in moral psychology is at best weak,
and if the theoretical argument for moral reframing is flawed,
why does moral reframing seem to work?